The skin Macmillan Cancer Support
This article will describe the anatomy and histology of the skin. Undoubtedly, the skin is the largest organ in the human body; literally covering you from head to toe. The organ constitutes almost 8-20% of body mass and has a surface area of approximately 1.6 to 1.8 m2, in an adult. It is comprised of three major layers: epidermis, dermis and.

Skin Structure (labelled), illustration Stock Image C043/4873
The skin has a surface area of between 16.1-21.5 sq ft. for an adult human. The thickness of the skin differs over all parts of the body, and between men and women and the young and the old. For example, the skin on the forearm which is on average 1.3 mm in the human male and 1.26 mm in the human female.
POSTECH University develops 3D bioprinting technique that grows human
The skin is the body's largest and primary protective organ, covering its entire external surface and serving as a first-order physical barrier against the environment. Its functions include temperature regulation and protection against ultraviolet (UV) light, trauma, pathogens, microorganisms, and toxins. The skin also plays a role in immunologic surveillance, sensory perception, control of.
Skin diagram labeled
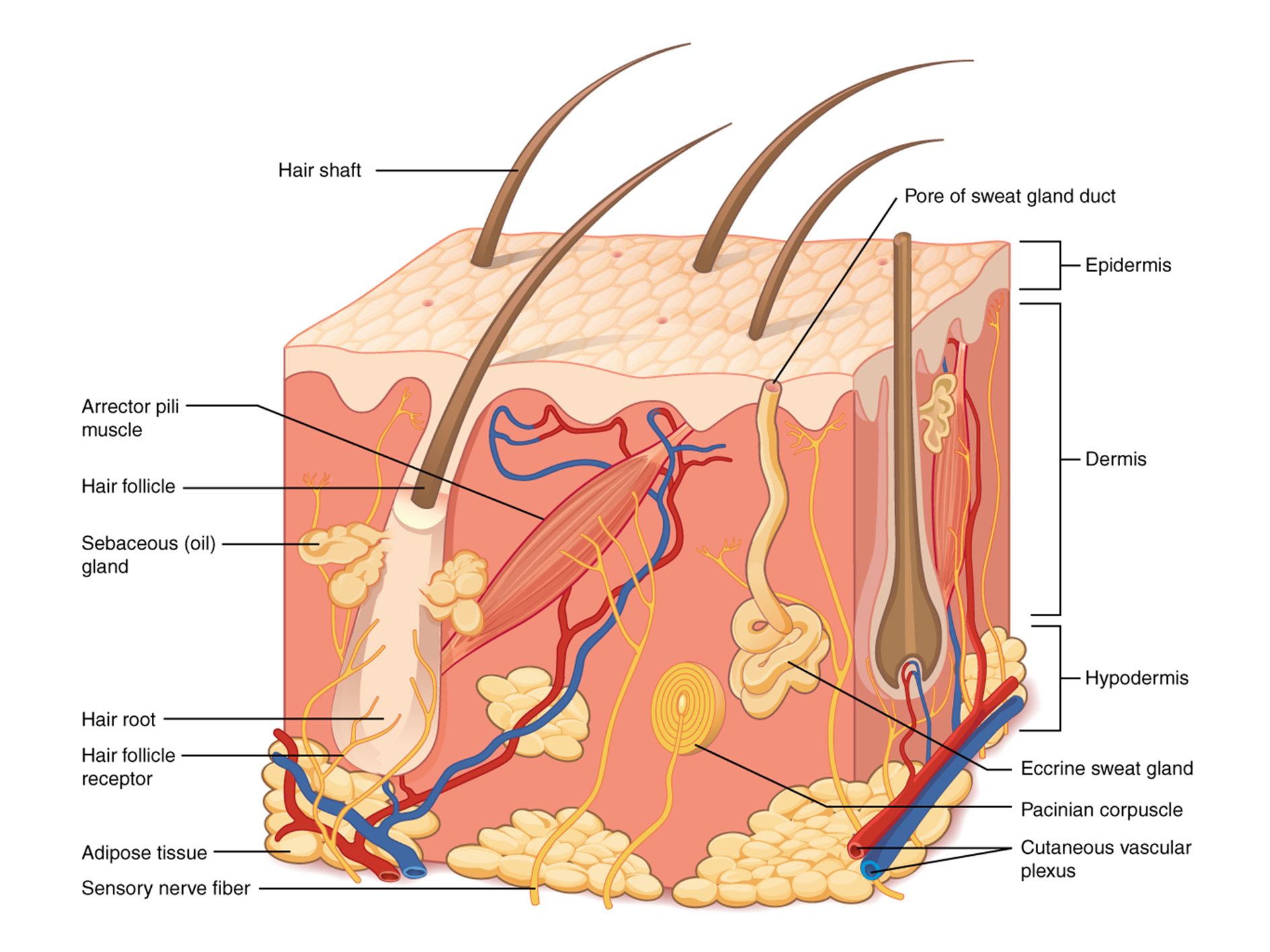
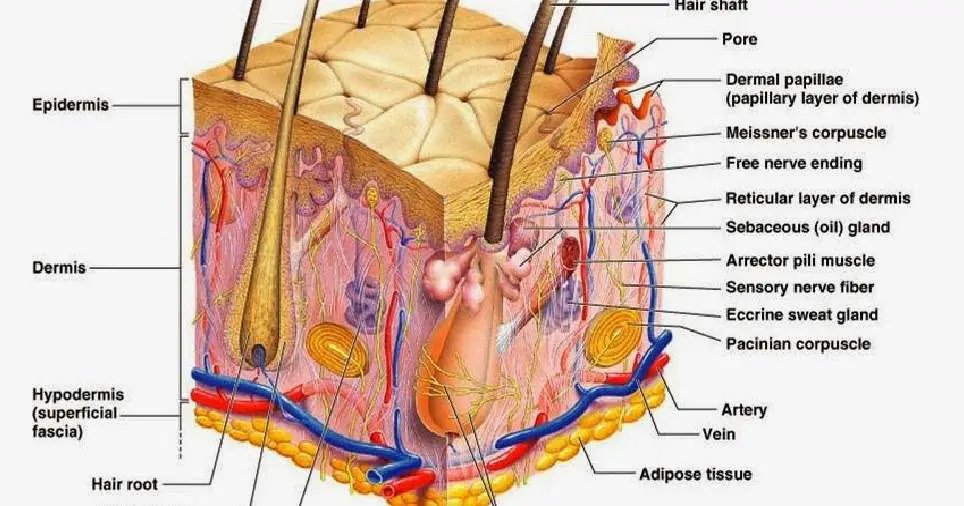
The skin has three basic layers, each with a different role. The number of skin layers that exists depends on how you count them. You have three main layers of skin—the epidermis , dermis, and hypodermis (subcutaneous tissue). Within these layers are additional layers. If you count the layers within the layers, the skin has eight or even 10.

why you may breakout with new skincare products? HydroSkinCare
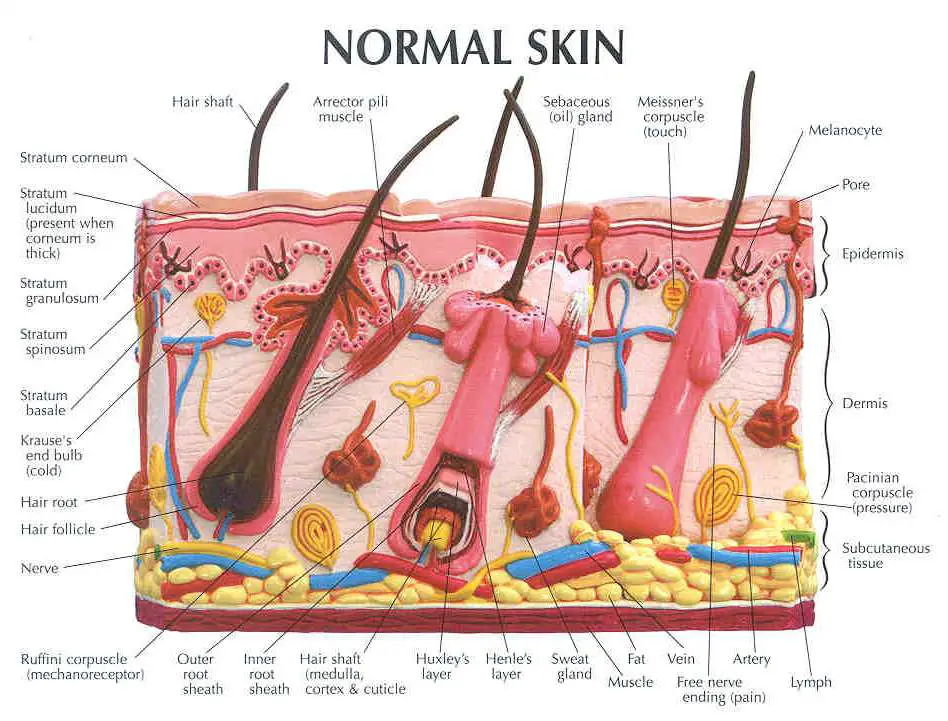
Key facts about the integumentary system; Skin: Functions: chemical and mechanical barrier, biosynthesis, control of body temperature, sensory Layers: Epidermis (Stratum Basale, Spinosum, Granulosum, Lucidum, Corneum) and dermis (papillary, reticular) Mnemonic: British and Spanish Grannies Love Cornflakes Hair: Types: vellus and terminal Structure: Follicle and bulb (shaft, inner root sheath.
Skin diagram labeled
The skin is the body's largest organ. It covers the entire body. It serves as a protective shield against heat, light, injury, and infection. The skin also: Regulates body temperature. Stores water and fat. Is a sensory organ. Prevents water loss. Prevents entry of bacteria.

Skin topical steroid withdrawal with wheatgrass extract A
The skin is composed of two main layers: the epidermis, made of closely packed epithelial cells, and the dermis, made of dense, irregular connective tissue that houses blood vessels, hair follicles, sweat glands, and other structures. Beneath the dermis lies the hypodermis, which is composed mainly of loose connective and fatty tissues.

Labelled Pictures Of Human Skin Layers of the Skin Biology I The
'Skin Diagram || How to draw and label the parts of skin' is demonstrated in this video tutorial step by step.The sense of touch had received supreme importa.
Skin diagram to label Labelled diagram
Diagram of human skin structure. Image. Add to collection. Rights: The University of Waikato Te Whare Wānanga o Waikato Published 1 February 2011 Size: 100 KB Referencing Hub media. The epidermis is a tough coating formed from overlapping layers of dead skin cells.

Skin Definition, Structure And Functions Of Skin
1. The outermost layer of the skin is: the dermis / the epidermis / fat layer. 2. Which is the thickest layer: the dermis / the epidermis? 3. Add the following labels to the diagram of the skin shown below: Epidermis, dermis, fat cells, hair shaft, hair follicle, hair erector muscle, sweat gland, pore of sweat gland, sebaceous gland, blood.

Skin Structure Diagram Best Picture Collection
Skin Diagram. The largest organ in the human body is the skin, covering a total area of about 1.8 square meters. The skin is tasked with protecting our body from external elements as well as microbes. The skin is also responsible for maintaining our body temperature - this was apparent in victims who were subjected to the medieval torture of.
Human Skin Structure, Useful Functions, and Interesting Facts Owlcation
This Osmosis High-Yield Note provides an overview of Skin Structures essentials. All Osmosis Notes are clearly laid-out and contain striking images, tables, and diagrams to help visual learners understand complex topics quickly and efficiently. Find more information about Skin Structures: Skin anatomy and physiology. Hair, skin and nails.

Human Anatomy Diagrams To Label koibana.info Skin anatomy, Human
Labeled diagram of the skin. So what's the idea? Spend some time analyzing the skin diagram labeled above. Try to memorize the appearance and location of each structure. Learning the function of each structure will accelerate your ability to memorize, so be sure to check out our detailed article on The Integumentary System parts and functions.
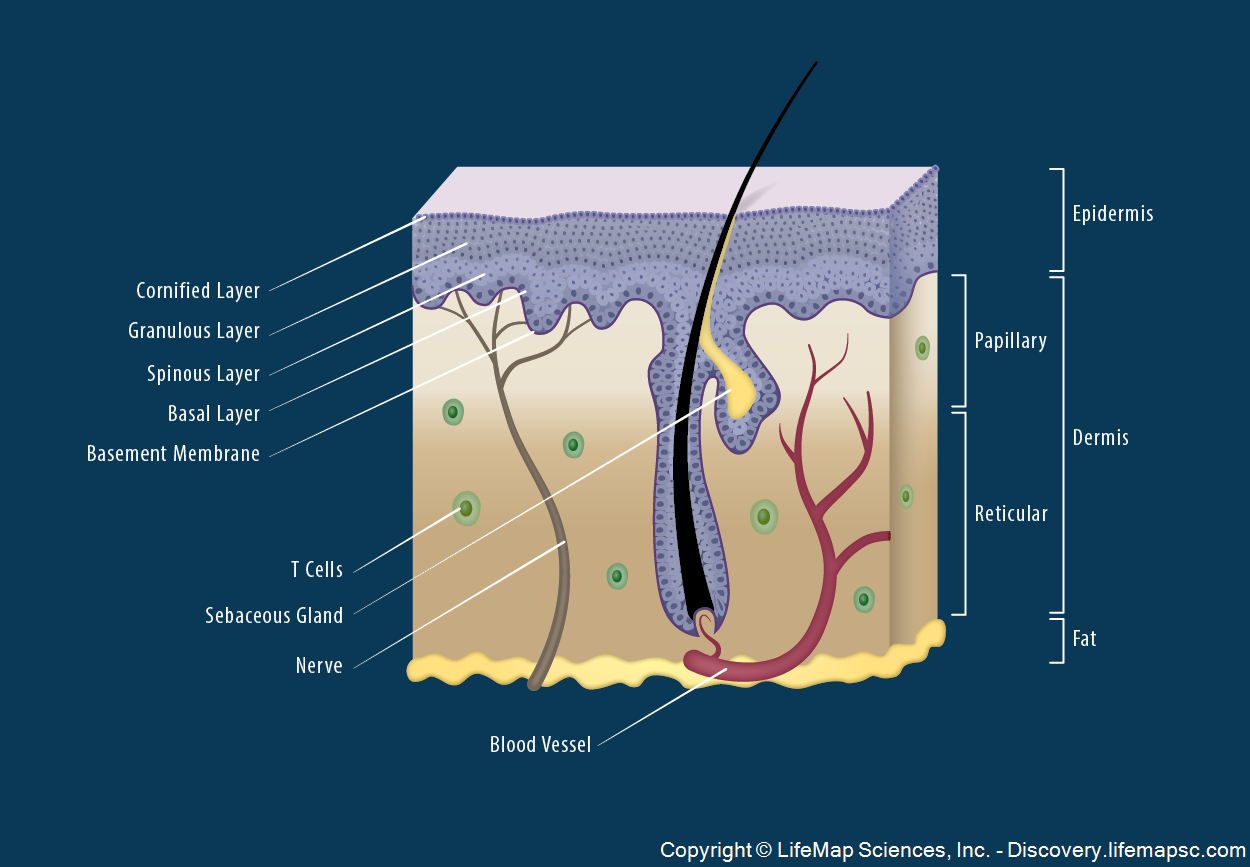
Skin Structure infographic LifeMap Discovery
The Layers of Your Skin. Your skin includes three layers known as epidermis, dermis, and fat. Some health issues, such as dermatitis and infections, can affect how these different layers work to.

Cross section anatomy of skin with labels on white background
The skin is by far the largest organ of the human body, weighing about 10 pounds (4.5 kg) and measuring about 20 square feet (2 square meters) in surface area. It forms the outer covering for the entire body and protects the internal tissues from the external environment. The skin consists of two distinct layers: the epidermis and the dermis.

Human skin diagram Anatomy and Physiology in 2018 Pinterest Skin
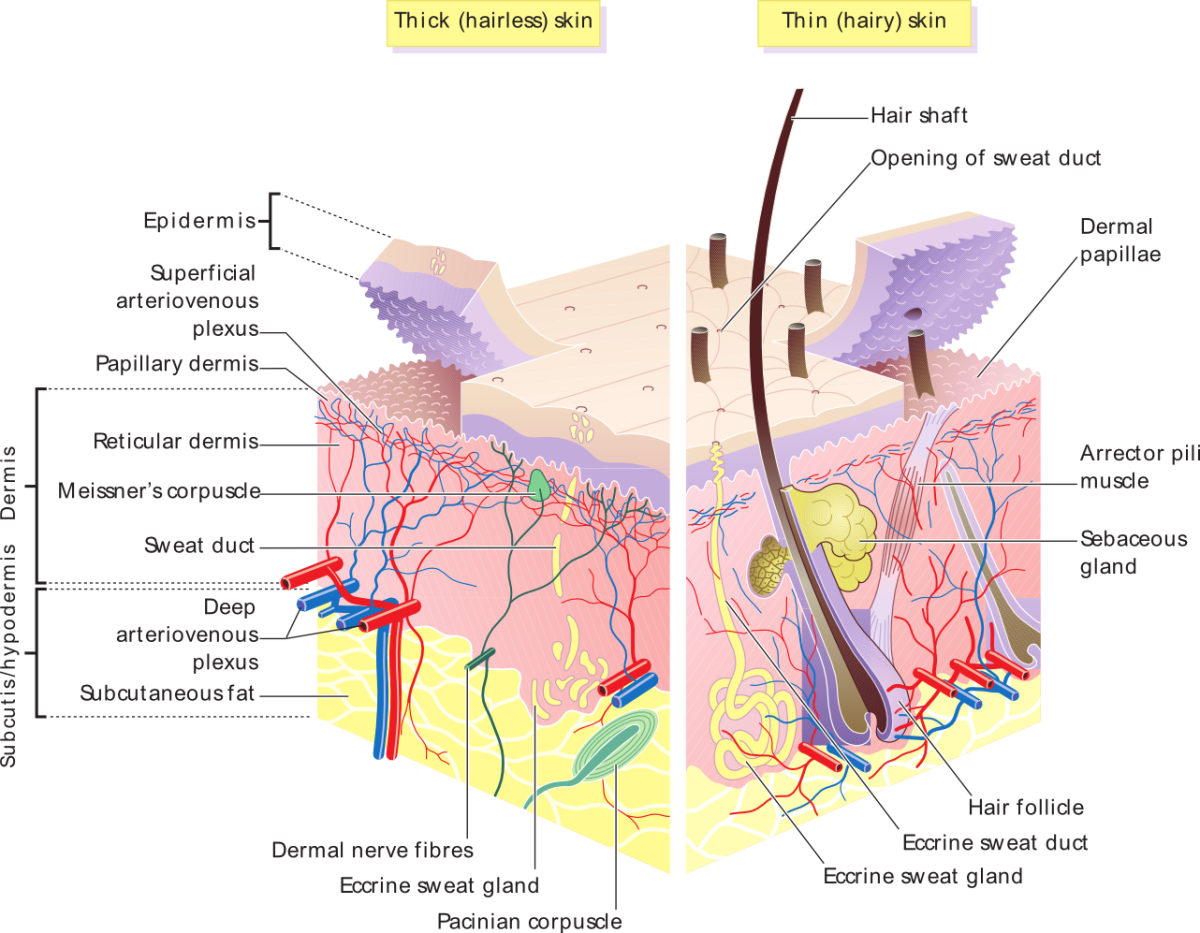
"Thick skin" is found only on the palms of the hands and the soles of the feet. It has a fifth layer, called the stratum lucidum, located between the stratum corneum and the stratum granulosum (Figure 5.1.2). Figure 5.1.2 - Thin Skin versus Thick Skin: These slides show cross-sections of the epidermis and dermis of (a) thin and (b) thick.