
Tropical cyclone Definition, Causes, Formation, and Effects Britannica
Tropical cyclones (or storms) are between 482-644 kilometres wide and 6-8 km high. They move forward at speeds of 16-24 km/h, but can travel as fast as 65 km/h.
Schema Electrique Typhoon Bois Eco Concept Fr My XXX Hot Girl
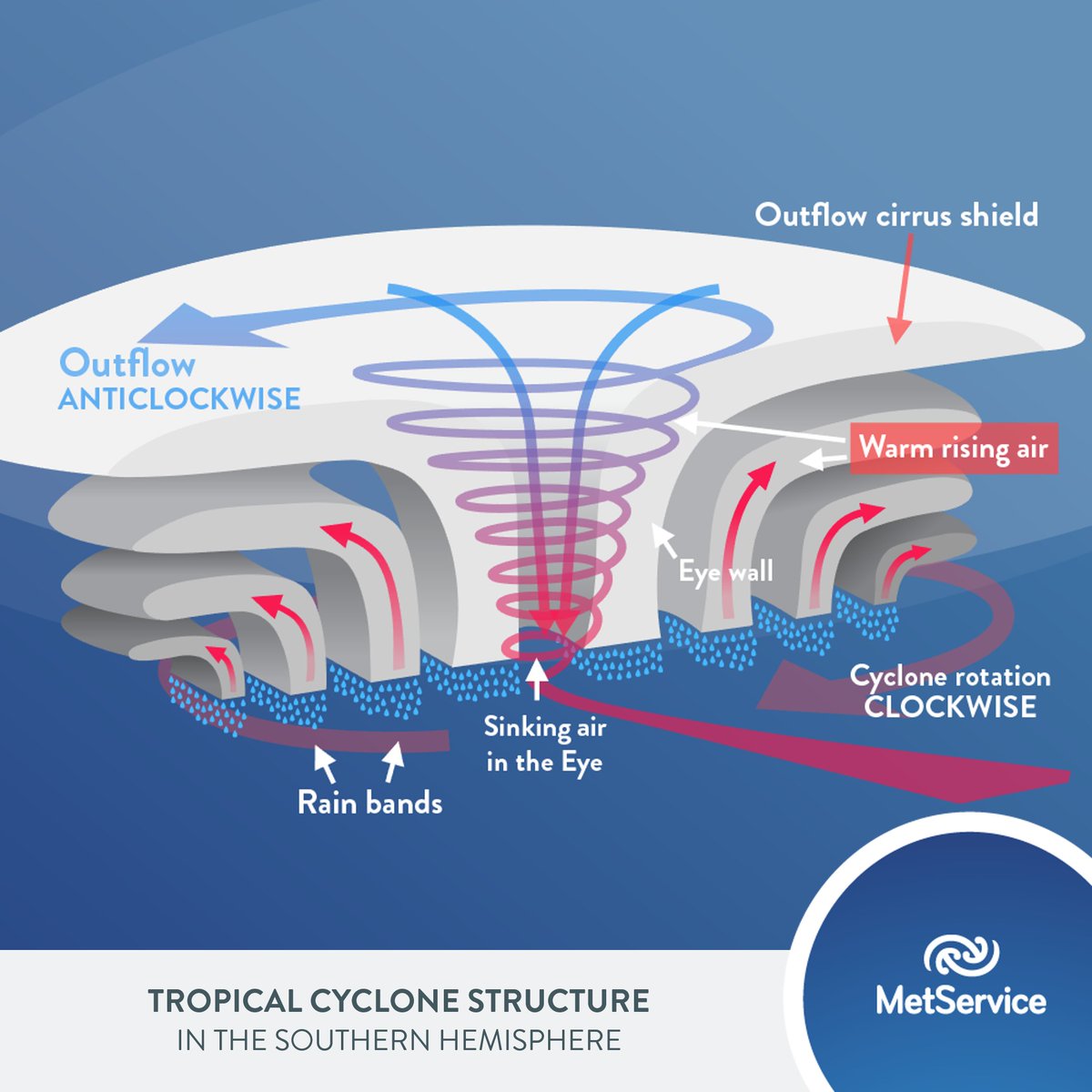
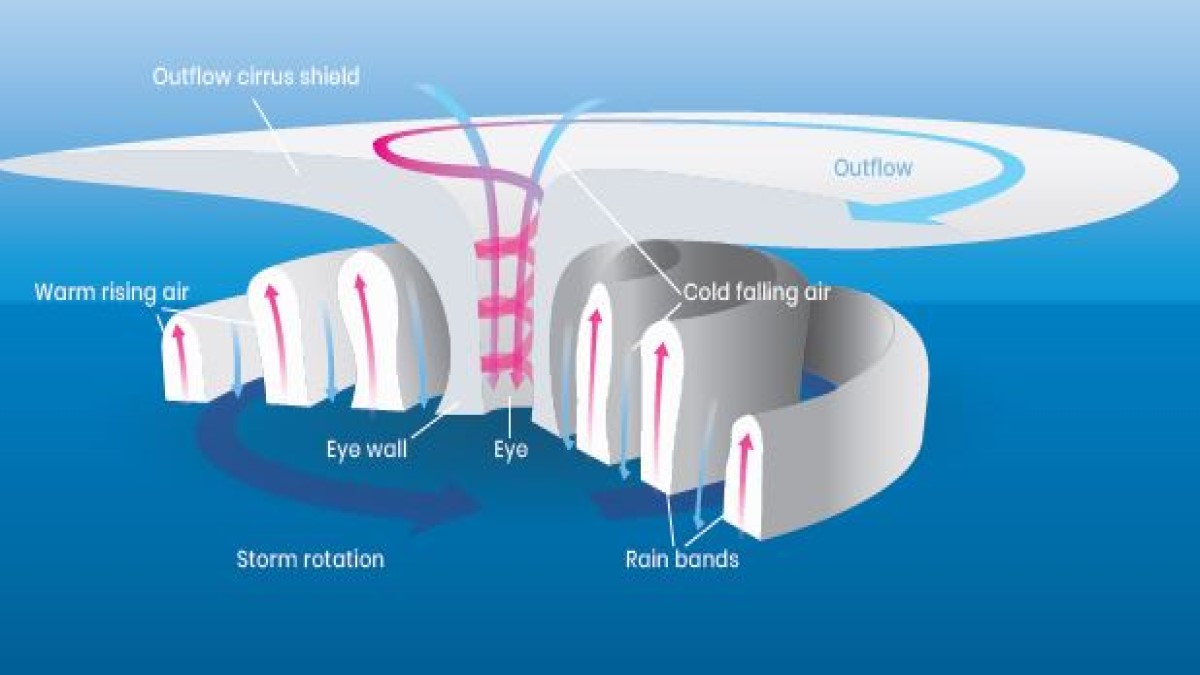
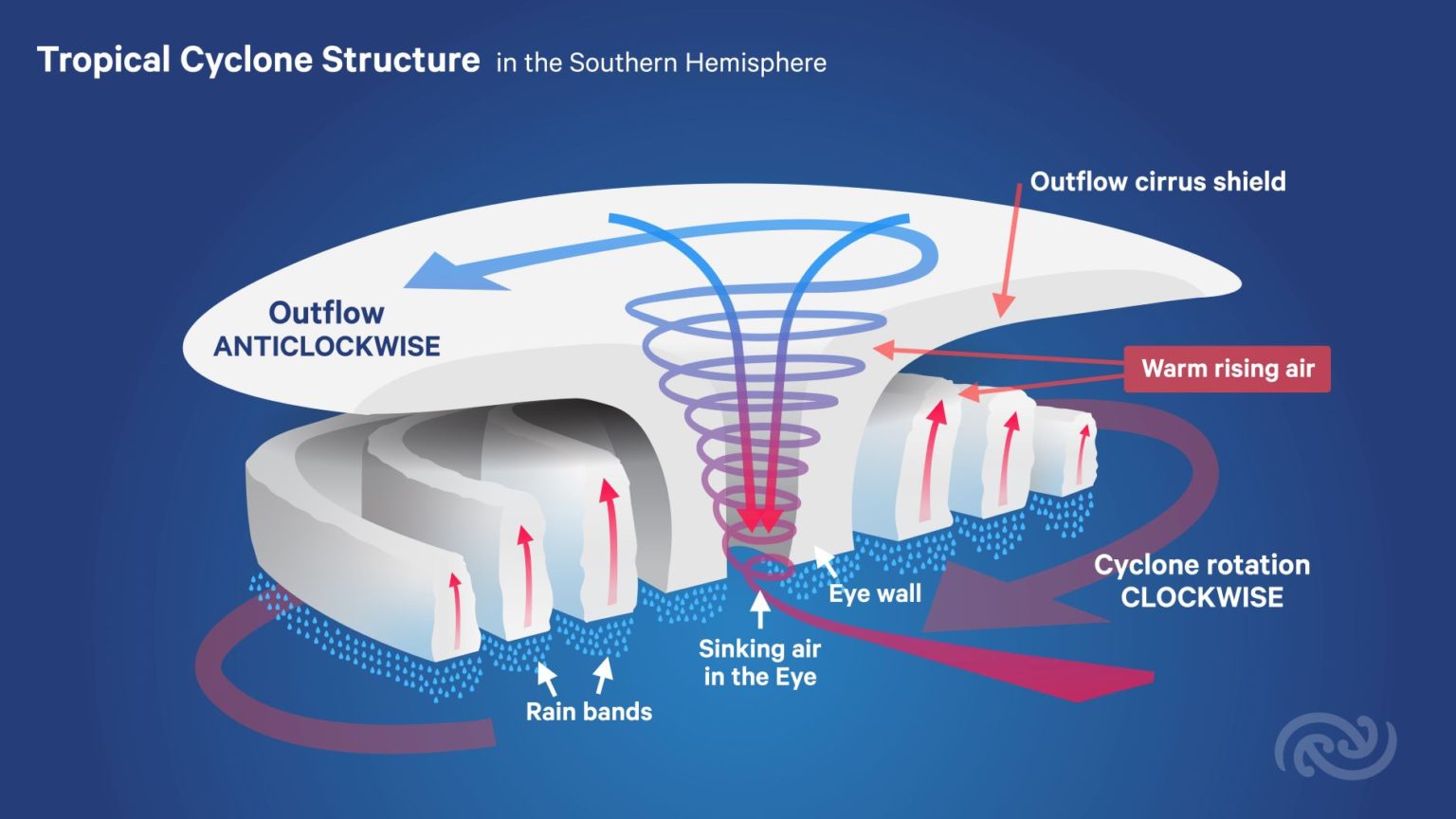
Diagram-1. Isobars in a low-pressure centre Characteristics of tropical cyclone Size of tropical cyclone- On average they are smaller than a temperate cyclone. Their diameter ranges between 500- 600 km. Sometimes their diameter is restricted to 50 km or even less.

Tropical Cyclones Affecting Perth
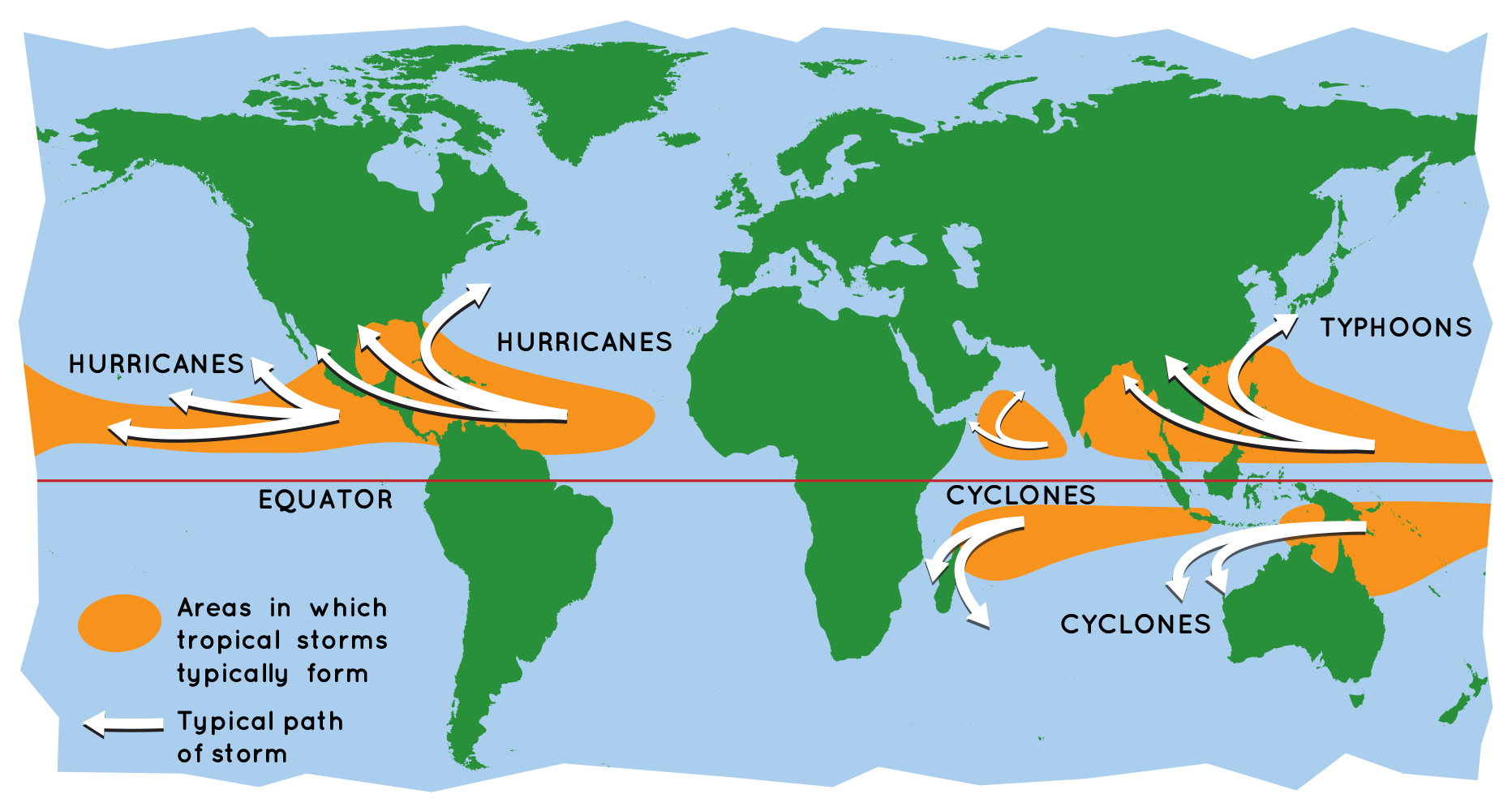
Tropical Cyclones Toolkit. Tropical cyclonic storms are low-pressure systems that form over warm tropical waters where sea surface temperatures are greater than 79°F (26°C). Because of this critical temperature, they occur in different seasons in the Atlantic, Pacific, and Indian Oceans. These massive storms bring sustained heavy wind and.
The Anatomy of a Tropical Cyclone Rayburn Tours
Diagram of a tropical cyclone system Rising seas lead to storm surges As well as damaging winds, a tropical cyclone can cause the sea to rise well above normal tide levels when it comes ashore. These storm surges are caused by strong, onshore waves or reduced atmospheric pressure—or both.

Characteristics of Cyclones GCSE Geography B Edexcel Revision Study Rocket
We recommend a multivariate historical assessment of tropical and subtropical cyclones across all basins in which they occur, including the South Atlantic Ocean and the Mediterranean Sea, to identify the potential for a more universal cyclone classification approach that meets operational needs. Keywords tropical cyclone subtropical cyclone
How Do Hurricanes Form? NASA Space Place NASA Science for Kids
A tropical cyclone is a rapidly rotating storm system characterized by a low-pressure center, a closed low-level atmospheric circulation, strong winds, and a spiral arrangement of thunderstorms that produce heavy rain and squalls.

5.5 Tropical Cyclones (Hurricanes) World Regional Geography
The long-term changes of ocean surface waves associated with tropical cyclones (TCs) are poorly observed and understood. Here, we present the global trend analysis of TC waves for 1979-2022.

Temperate and Extratropical Cyclones Life Cycle and Stages UPSC IAS
Tropical Cyclone formation regions with mean tracks (courtesy of the NWS JetStream Online School) Atlantic and Eastern Pacific Hurricane Season Normal Activity. The Atlantic hurricane season runs from June 1 to November 30. The Atlantic basin includes the Atlantic Ocean, Caribbean Sea, and Gulf of Mexico. Based on a 30-year climate period from.

LABORATORY 4 MIDLATITUDE CYCLONES, WEATHER MAPS, AND FORECASTING Physical Geography Lab
A tropical cyclone is a warm-core low pressure system, without any front attached, that develops over the tropical or subtropical waters and has an organized circulation. These include hurricanes and typhoons. There are several favorable environmental conditions that must be in place before a tropical cyclone can form.
/cloudfront-us-east-1.images.arcpublishing.com/gray/6JFZKMEX6ZABFKHJKRGYDVXYR4.PNG)
Breakdown Why the eye of a hurricane is calm, but still deadly
A tropical disturbance occurs when warm water vapor rises off the ocean into the atmosphere, condensing into large cloud columns as it cools. As more water vapor rises and condenses, the cloud columns become larger and taller with wind spiraling around their center. These cloud columns eventually cluster together, forming into thunderstorms.

The classic diagram of a mature tropical cyclone (after Palmén and... Download Scientific Diagram
Tropical cyclones (TCs), one of the weather systems may pose catastrophic and even lethal natural disaster risks to human societies, which are kinds of intense and deep warm atmospheric vortices.
Tropical cyclones Expert Q&A Science Media Centre
Formation | Easterly Wave. Tropical cyclones often develop along easterly waves. These waves, or oscillations, in the trade winds move from east to west across the tropics. Satellite imagery provides the best view of an easterly wave. As low-level winds enter the trough of the wave, they converge, causing convection. Overlay the satellite.
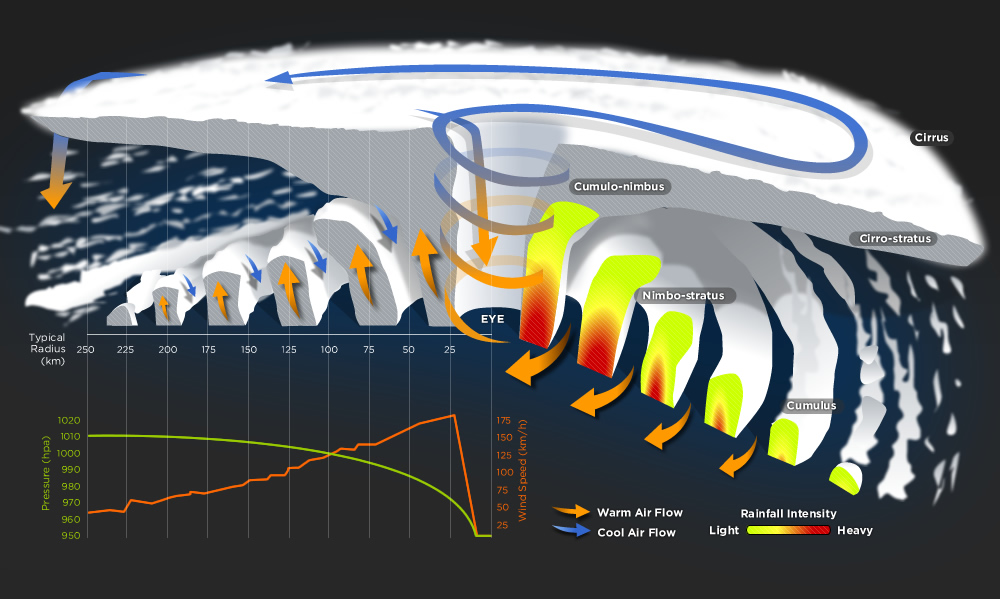
Explain Cyclone Testing Station FarLabs
tropical cyclone, an intense circular storm that originates over warm tropical oceans and is characterized by low atmospheric pressure, high winds, and heavy rain. Drawing energy from the sea surface and maintaining its strength as long as it remains over warm water, a tropical cyclone generates winds that exceed 119 km (74 miles) per hour.

tropical cyclone Life of a cyclone Britannica
Access lesson resources for this video + more high school geography videos for free on ClickView https://clickv.ie/w/7aAw#cyclones #hurricanes #typhoons #g.
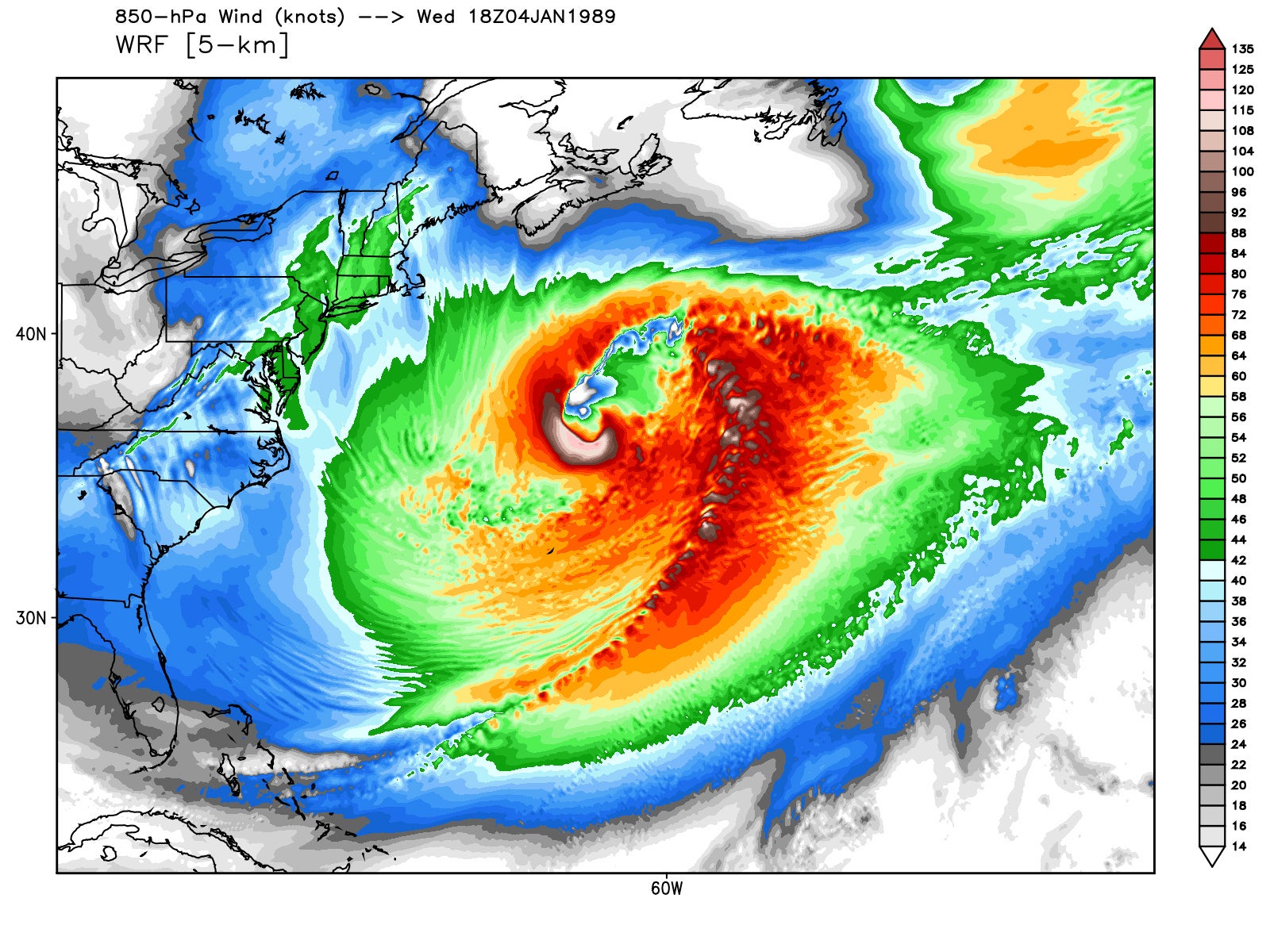
√ Tropical Cyclone Diagram Causes Of Tropical Cyclones Geography Myp Gcse Dp The tropical
This page presents historical, analyzed (current), and model-forecast cyclone phase diagrams for northwestern hemisphere cyclones with the goals of improved structural forecasting, structural transition (subtropical/tropical/extratropical), cyclogenesis, and providing measures of structural predictability.
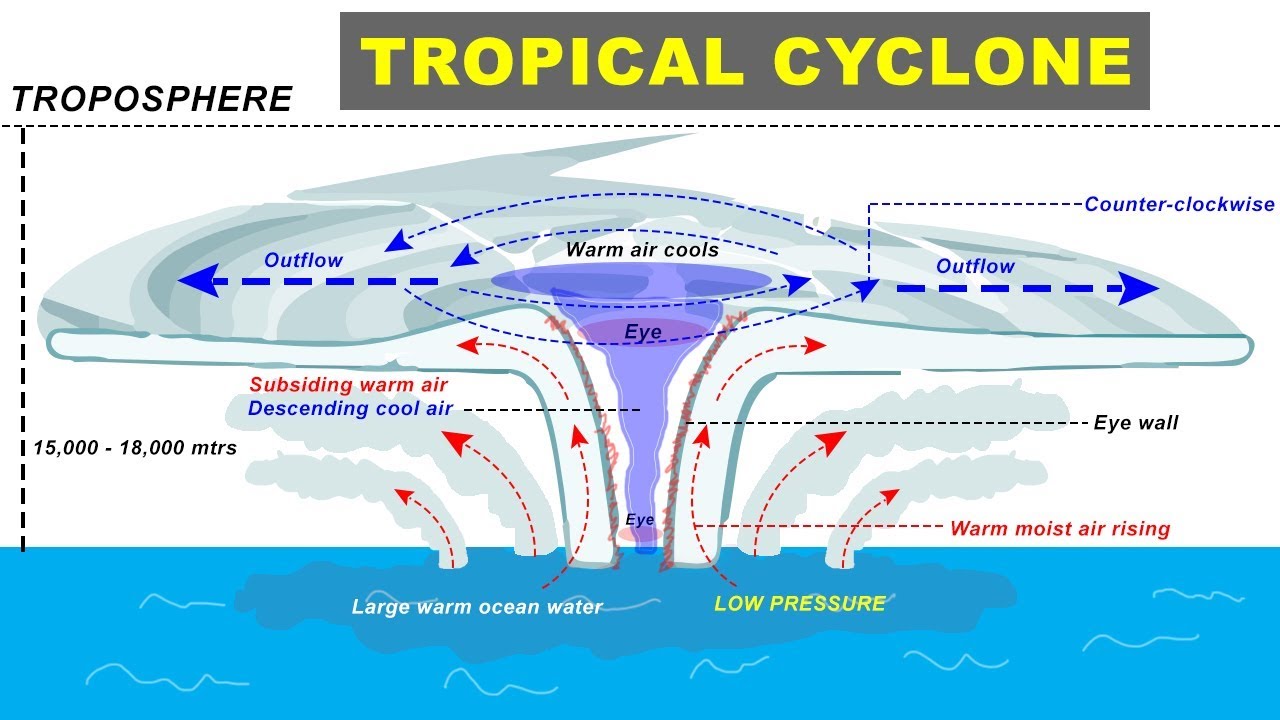
Tropical Cyclone Formation / Tropical Storm Risk Cyclocane / Tropical cyclone, an intense
Here are the Tropical Cyclone Diagram given below: Tropical Cyclone Formation There are some necessary conditions that favour the formation and intensification of tropical storms are: A large area of the sea surface with a temperature greater than 27° C. Presence of Coriolis force. Variations in vertical wind speed are minor.